

SuDS-related links
Keeping ahead
with SuDS
Attend SuDS training to keep ahead of the competition and to deliver innovative solutions in line with recognised good practice.
home > using SuDS > background
Drainage systems can be developed to contribute to sustainable development and improve urban design, by balancing the different issues that should be influencing the development of communities. Surface water drainage methods that take account of water quantity, water quality and amenity issues are collectively referred to as Sustainable Drainage Systems (SuDS). SuDS are a sequence of management practices, control structures and strategies designed to efficiently and sustainably drain surface water, while minimising pollution and managing the impact on water quality of local water bodies. These systems are more sustainable than conventional drainage methods because they:
|
Figure 1 demonstrates the impacts of urbanisation on a catchment by increasing surface water runoff. This reduces opportunities for water to be managed naturally with the potential for pollution and localised flooding when the piped systems cannot cope with rainfall.
Figure 1: Effects of urbanisation on the water cylce |
SuDS may also allow new development in areas where existing sewerage systems are close to full capacity, thereby enabling development within existing urban areas.
Urban drainage is moving away from the conventional thinking of designing for flooding to balancing the impact of urban drainage on flood control, water quality management and amenity.
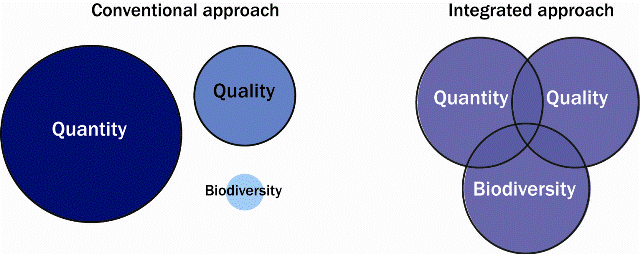
Sustainable drainage is a concept that includes long term environmental and social factors in decisions about drainage. It takes account of the quantity and quality of runoff, and the amenity and asthetic value of surface water in the urban environment. Many existing urban drainage systems can cause problems of flooding, pollution or damage to the environment and are not proving to be sustainable in the context of wider challenges from climate change and urbanisation.
Built-up areas need to be drained to remove surface water runoff. Traditionally this has been done using underground pipe systems designed for quantity, to prevent flooding locally by conveying the water away as quickly as possible. The alteration of natural flow patterns can lead to problems elsewhere in the catchment. Water quality issues have become increasingly important, due to pollutants from urban areas being washed into rivers or the groundwater. Once polluted, groundwater is extremely difficult to clean up. Traditional drainage systems cannot easily control poor runoff quality and may contribute to the problem. The amenity aspects, such as water resources, community facilities, landscaping potential and provision of varied wildlife habitats have largely been ignored. Traditional drainage systems are not designed with these wider considerations in mind.